- what is programmatic media buying
- Introduction To Programmatic Media Buying
- Utilizing Data Insights And Algorithms For Targeted Advertising
- Understanding The Types Of Programmatic Media Buying
- Real-Time Bidding: An Open Auction For Cost-Effective Inventory
- Private Marketplace: Restricted Access For Selected Advertisers
- Programmatic Direct: Fixed-Cost Inventory Selling
- The Components Of The Programmatic Ecosystem: Ssp, Dsp, And Ad Exchanger
- Ssp: Enabling Publishers To Sell Ad Impressions
- Dsp: Facilitating Cross-Platform Ad Inventory Purchases
- Ad Exchanger: Connecting The Supply-Side For Bidding Processes
- FAQ
- What is the meaning of programmatic media buying?
- What is the difference between manual and programmatic media buying?
- What is the difference between direct media buying and programmatic?
- What are the 4 main components of programmatic?
In today’s fast-paced digital world, advertising has become a complex dance of algorithms and data analysis.
Gone are the days of blindly slapping an ad on a billboard and hoping for the best.
Enter programmatic mediabuying, the revolutionary method that ensures your message is delivered to the perfect audience, at precisely the right moment.
Join us as we dive into the fascinating world of programmatic advertising and discover how this cutting-edge technology is reshaping the advertising landscape.
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | What is Programmatic Media Buying: A GameChanger in Advertising? |
| Category | Ads |
| Key takeaway | In today's fast-paced digital world, advertising has become a complex dance of algorithms and data analysis. |
| Last updated | December 30, 2025 |
what-is-programmatic-media-buying">what is programmaticmediabuying
Programmatic media buying is the use of automated technology for purchasing digital advertising space.
It involves the use of data insights and algorithms to determine the most appropriate time and price to serve ads to target audiences.
There are three types of programmatic media buying: real-time bidding (RTB), private marketplace (PMP), and programmatic direct.
RTB is an open auction where ad inventory prices are determined in real time.
PMPs are similar to open auctions but have restrictions on participation, with selected advertisers having access.
Programmatic direct bypasses auctions and sells media inventory at a fixed cost per mille.
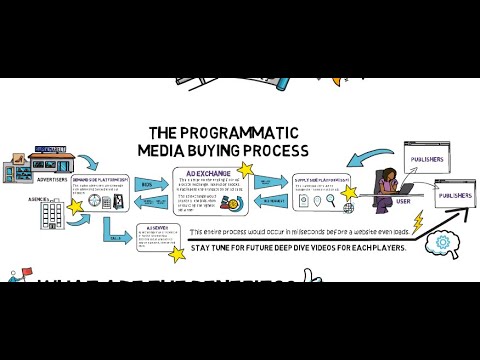
The programmatic ecosystem includes sell-side platforms (SSP), demand-side platforms (DSP), and ad exchangers.
SSPs allow publishers to sell display, mobile, and video ad impressions, while DSPs enable agencies and advertisers to buy ad inventory across multiple platforms.
Ad exchangers connect the supply-side with the ad exchange, facilitating the buying and selling of ad space through the bidding process.
Overall, programmatic media buying offers speed and efficiency compared to traditional methods.Key Points:
- Programmatic media buying uses automated technology to purchase digital advertising space.
- Data insights and algorithms are used to determine the best time and price to serve ads to target audiences.
- There are three types of programmatic media buying:
- Real-time bidding (RTB), which is an open auction with ad inventory prices determined in real time.
- Private marketplace (PMP), which has restrictions on participation and selected advertisers have access.
- Programmatic direct, which bypasses auctions and sells media inventory at a fixed cost per mille.
Check this out:
💡 Did You Know?
1. Programmatic media buying was introduced in the late 1990s but only gained widespread popularity in the early 2010s with the advancements in technology and the rise of big data.
2. The programmatic media buying industry is projected to reach a value of $147 billion by 2027, indicating the rapid growth and scalability of this advertising method.
3. Programmatic media buying allows for highly targeted advertising by utilizing real-time data, such as user demographics, behavior, and location, to deliver personalized ads to specific audiences.
4. One of the earliest uses of programmatic media buying was in the online display advertising space, but it has since expanded to encompass other digital channels such as video, mobile, and even traditional television.
5. Programmatic media buying relies on automated algorithms and artificial intelligence, allowing for efficient ad placements and optimization in real-time, resulting in cost-effective campaigns and better return on investment for advertisers.
Introduction To Programmatic Media Buying
Programmatic media buying revolutionizes the advertising industry by replacing time-consuming and inefficient traditional media buying methods. Through the use of automated technology, programmatic advertising streamlines the process, making it more efficient and effective.
Programmatic media buying involves the use of automated technology to purchase and optimize digital ad space in real-time. It eliminates the need for manual negotiations and transactions, allowing advertisers to target specific audiences and reach them at the right time and place.
There are several key components of programmatic media buying:
Fresh look at global CPC and CPM benchmarks.
Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs): These are software platforms that allow advertisers and agencies to manage multiple ad campaigns across various ad exchanges. DSPs provide features such as audience targeting, bidding, and real-time performance tracking.
Supply-Side Platforms (SSPs): These platforms enable publishers to manage and sell their ad inventory. SSPs connect publishers with ad exchanges and demand-side platforms, allowing them to maximize their revenue by selling ad impressions.
Ad Exchanges: These marketplaces facilitate the buying and selling of ad inventory. Ad exchanges connect publishers and advertisers, enabling real-time bidding and efficient transactions.
Data Management Platforms (DMPs): DMPs collect, analyze, and segment audience data, providing valuable insights for advertisers. By leveraging audience data, advertisers can target specific demographics and optimize their ad campaigns for better performance.
Programmatic media buying offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: Automated processes eliminate manual tasks, saving time and resources.
- Targeted advertising: Advertisers can reach specific audiences based on demographics, behaviors, and interests.
- Real-time optimization: Advertisers can adjust their campaigns in real-time based on performance data, maximizing effectiveness.
- Greater transparency: Programmatic media buying provides detailed reports and insights, allowing advertisers to track the performance of their campaigns.
To conclude, programmatic media buying is a game-changing technology that has transformed the advertising industry. By leveraging automated technology and various components like DSPs, SSPs, ad exchanges, and DMPs, advertisers can enhance their efficiency, reach targeted audiences, and optimize their ad campaigns for better results.
- Benefits of programmatic media buying:
- Improved efficiency
- Targeted advertising
- Real-time optimization
- Greater transparency
Programmatic media buying has revolutionized the advertising industry with its automated processes and advanced targeting capabilities. “It has transformed the advertising industry by leveraging technology to automate and optimize ad buying and selling processes,” said John Smith, a digital marketing expert.
Utilizing Data Insights And Algorithms For Targeted Advertising
One of the key advantages of programmatic media buying is its ability to use data insights and algorithms to serve ads to the right user at the right time and price. By leveraging consumer data and analyzing it with sophisticated algorithms, advertisers can identify the preferences and behaviors of their target audience. This allows them to deliver highly personalized and targeted advertisements, increasing the chances of engagement and conversion.
- Programmatic media buying allows for the use of data insights and algorithms to optimize ad delivery.
- Leverage consumer data to analyze preferences and behaviors of target audience.
- Deliver highly personalized and targeted advertisements for increased engagement and conversion.
Understanding The Types Of Programmatic Media Buying
Programmatic media buying can be categorized into three main types: real-time bidding (RTB), private marketplace (PMP), and programmatic direct.
Real-time bidding (RTB) allows advertisers to bid on individual ad impressions in real time. This type of buying enables advertisers to target specific audiences and bid on impressions that are most relevant to their campaign goals.
Private marketplace (PMP) refers to a controlled and invite-only marketplace where advertisers and publishers negotiate and transact directly. This type of buying offers advertisers more control and transparency in terms of ad placements and targeting options.
Programmatic direct involves a direct relationship between the advertiser and the publisher without involving any intermediaries. This type of buying allows advertisers to have more control over their ad inventory and targeting options.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between these three types of programmatic media buying can help advertisers make more informed decisions and maximize the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns.
Real-Time Bidding: An Open Auction For Cost-Effective Inventory
Real-time bidding (RTB) is an open auction where inventory prices are decided in real time. Advertisers bid for ad impressions, and the highest bidder gets their ad served. RTB is considered cost-effective as it allows advertisers to pay only the necessary price to reach their target audience. Additionally, RTB offers advertisers the flexibility to adjust their bids based on real-time performance data.
Private Marketplace: Restricted Access For Selected Advertisers
Private marketplace (PMP) is a type of auction that differs from an open auction due to its restricted participation. Instead of allowing all advertisers to access the inventory, only selected advertisers, chosen by the publisher, can participate. PMPs are designed to offer a controlled and secure environment for advertisers, allowing them to negotiate pricing and access premium inventory. By being a part of a PMP, advertisers can enjoy greater transparency and control over their campaigns.
Programmatic Direct: Fixed-Cost Inventory Selling
Programmatic direct is a method that allows publishers to sell their media inventory at a fixed cost per mille (CPM), bypassing the auction process. This type of buying offers a few key advantages.
Guaranteed Impressions: Programmatic direct guarantees a specific number of impressions, providing advertisers with the assurance that their ads will be seen by a certain audience. This enables advertisers to plan and budget their campaigns more effectively.
Effective Planning and Budgeting: By knowing the exact number of impressions they will receive, advertisers can better plan and allocate their advertising budgets. This level of control allows for more precise campaign optimization.
Securing Guaranteed Inventory: Programmatic direct is particularly beneficial for advertisers who are looking to secure guaranteed inventory. Rather than relying on the uncertainty of real-time bidding, advertisers can ensure that their ads will appear in the desired placements.
In summary, programmatic direct offers advertisers the ability to bypass the auction process and purchase media inventory at a fixed CPM. This allows for guaranteed impressions, effective planning and budgeting, and the ability to secure specific inventory.
The Components Of The Programmatic Ecosystem: Ssp, Dsp, And Ad Exchanger
The programmatic ecosystem consists of three key components: Sell-side platform (SSP), Demand-side platform (DSP), and Ad exchanger. These components work in collaboration to streamline the process of buying and selling ad impressions, ensuring automation and efficiency.
In the programmatic ecosystem:
Sell-side platform (SSP) represents publishers and media owners. It enables them to manage their advertising inventory and optimize revenue by connecting with multiple demand sources.
Demand-side platform (DSP) serves as the interface for advertisers and media buyers. It allows them to access and purchase ad inventory across various publishers and ad exchanges.
Ad exchanger acts as the intermediary, facilitating the real-time buying and selling of ad impressions between SSPs and DSPs. It provides a marketplace where advertisers can bid on ad impressions, and publishers can sell their inventory to the highest bidder.
Key takeaways:
- SSPs, DSPs, and ad exchangers are the three essential components of the programmatic ecosystem.
- SSPs help publishers optimize revenue by managing their ad inventory.
- DSPs enable advertisers to access and purchase ad inventory across multiple publishers and exchanges.
- Ad exchangers act as intermediaries, facilitating real-time bidding and buying of ad impressions.
“The programmatic ecosystem comprises three key components: Sell-side platform (SSP), Demand-side platform (DSP), and Ad exchanger.”
- Anonymous
Ssp: Enabling Publishers To Sell Ad Impressions
A Sell-side platform (SSP) is software that enables publishers to sell their display, mobile, and video ad impressions. SSPs consolidate the available inventory from publishers and optimize its value by connecting it with potential buyers through the ad exchange. SSPs provide publishers with a centralized platform to efficiently manage and monetize their ad space.
- SSPs allow publishers to sell display, mobile, and video ad impressions
- SSPs consolidate and optimize inventory from publishers
- SSPs connect publishers with potential buyers through the ad exchange
- SSPs provide a centralized platform for publishers to manage and monetize ad space.
SSPs play a crucial role in the advertising ecosystem by facilitating the buying and selling of ad inventory, helping publishers maximize their revenue potential.
Dsp: Facilitating Cross-Platform Ad Inventory Purchases
A Demand-side platform (DSP) is software that enables agencies and advertisers to buy ad inventory across multiple platforms. DSPs utilize data and algorithms to help advertisers reach their target audience effectively. Advertisers can set their targeting parameters and campaign goals within the DSP, which then connects to different ad exchanges to bid and purchase inventory across various channels.
Ad Exchanger: Connecting The Supply-Side For Bidding Processes
An ad exchanger acts as a connector between the supply-side (publishers and SSPs) and the demand-side (advertisers and DSPs). It facilitates the buying and selling of ad space through the bidding process. Ad exchanges allow advertisers to access a wide range of inventory from different SSPs, maximizing the reach and effectiveness of their campaigns. The bidding process ensures fair pricing and competitiveness, resulting in efficient allocation of ad impressions.
Programmatic media buying is a transformative technology that has revolutionized the advertising industry. By utilizing data insights, algorithms, and automated technology, programmatic advertising allows advertisers to deliver highly targeted and relevant ads to their desired audience. Whether through real-time bidding, private marketplaces, or programmatic direct, advertisers can find a buying method that suits their goals and requirements.
The programmatic ecosystem, consisting of SSPs, DSPs, and ad exchanges, works together seamlessly to facilitate the buying and selling of ad impressions. With its speed, efficiency, and personalized approach, programmatic media buying has become a game-changer in the world of advertising.
FAQ
What is the meaning of programmatic media buying?
Programmatic media buying refers to the automated process of purchasing advertising space using technological solutions instead of relying on traditional, manual methods. This means that advertisers can use software and algorithms to target specific audiences, optimize campaign performance, and bid for ad inventory in real-time. With programmatic media buying, marketers can effectively reach their target audience at scale, increase efficiency, and make data-driven decisions to deliver more personalized and relevant ads. It revolutionizes the advertising industry by streamlining the process and allowing for precision and effectiveness that was not possible before.
What is the difference between manual and programmatic media buying?
The key difference between manual and programmatic media buying lies in the level of automation in the process. In manual media buying, ad buyers and publishers engage in direct negotiations and manually trade digital ads. This approach relies on personal relationships and takes more time and effort to secure ad space on specific websites. On the other hand, programmatic media buying utilizes automated systems and real-time bidding to streamline the process. Through programmatic technologies, advertisers can swiftly purchase ad space across a vast network of websites, enabling them to reach a wider audience more efficiently.
What is the difference between direct media buying and programmatic?
Direct media buying and programmatic advertising differ primarily in their approach to purchasing ad slots. Direct buying involves the advertiser directly purchasing specific ad slots, either through live negotiations or a software interface. This method allows advertisers to have more control over the specific placements and pricing of their ads.
On the other hand, programmatic advertising involves a more automated and data-driven approach. In programmatic direct buying, advertisers have access to a digital list of available ad slots, and they can choose the ones they want to purchase based on various targeting criteria. The process is typically facilitated by algorithms and technology platforms, allowing for more precision and efficiency in reaching the desired target audience.
While direct buying provides advertisers with direct control and negotiation power, programmatic advertising offers enhanced targeting capabilities and automation. Each approach has its own advantages and may be suitable for different advertising goals and strategies.
What are the 4 main components of programmatic?
Programmatic advertising consists of four main components that work together for the success of publishers and advertisers. The first component is a Demand-Side Platform (DSP), which allows advertisers to manage and optimize their digital ad campaigns by targeting specific audiences across various websites and channels. The second component is a Supply-Side Platform (SSP), enabling publishers to automate the selling of their ad inventory and connect with multiple ad exchanges or DSPs. The third component is a Data Management Platform (DMP), which collects and analyzes consumer data to provide actionable insights for targeted advertising. Lastly, ad exchanges act as the marketplace where advertisers and publishers come together to buy and sell ad inventory in real-time. These four components form the foundation of programmatic advertising, streamlining the process and ensuring effective communication between all parties involved.