- stp marketing mix
- What Is STP Marketing And How Does It Work?
- Importance Of Personalization In Marketing Decisions
- Segmentation: Identifying Customer Segments Based On Criteria
- Targeting: Tailoring Marketing Campaigns To Specific Customer Segments
- Positioning: Adjusting The Marketing Mix To Match The Target Audience
- Benefits Of Using STP Marketing For Hyper-Personalization
- STP Marketing For Small Businesses And Startups
- Steps To Creating A Marketing Strategy Using The STP Model
- Positioning Strategies For Effective Marketing
- FAQ
- What is STP in the marketing mix?
- What is the relationship between STP and 4Ps?
- What is an example of STP targeting?
- What are the 4 segmentation variables?
In a world overflowing with options, grabbing consumers’ attention has become an art form.
That’s where STPmarketing comes into play, helping businesses cut through the noise by crafting personalized campaigns.
By mastering the art of segmentation, targeting, and positioning, companies can unlock the secret to captivating their desired audience and unleashing the true potential of their marketing efforts.
So, sit tight and discover the power of STP marketing mix in this captivating journey ahead.
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | The Ultimate Guide to Optimizing your STP Marketing Mix: Strategies, Tips, and Best Practices |
| Category | Marketing |
| Key takeaway | In a world overflowing with options, grabbing consumers' attention has become an art form. |
| Last updated | December 29, 2025 |
stp-marketing-mix">stp marketing mix
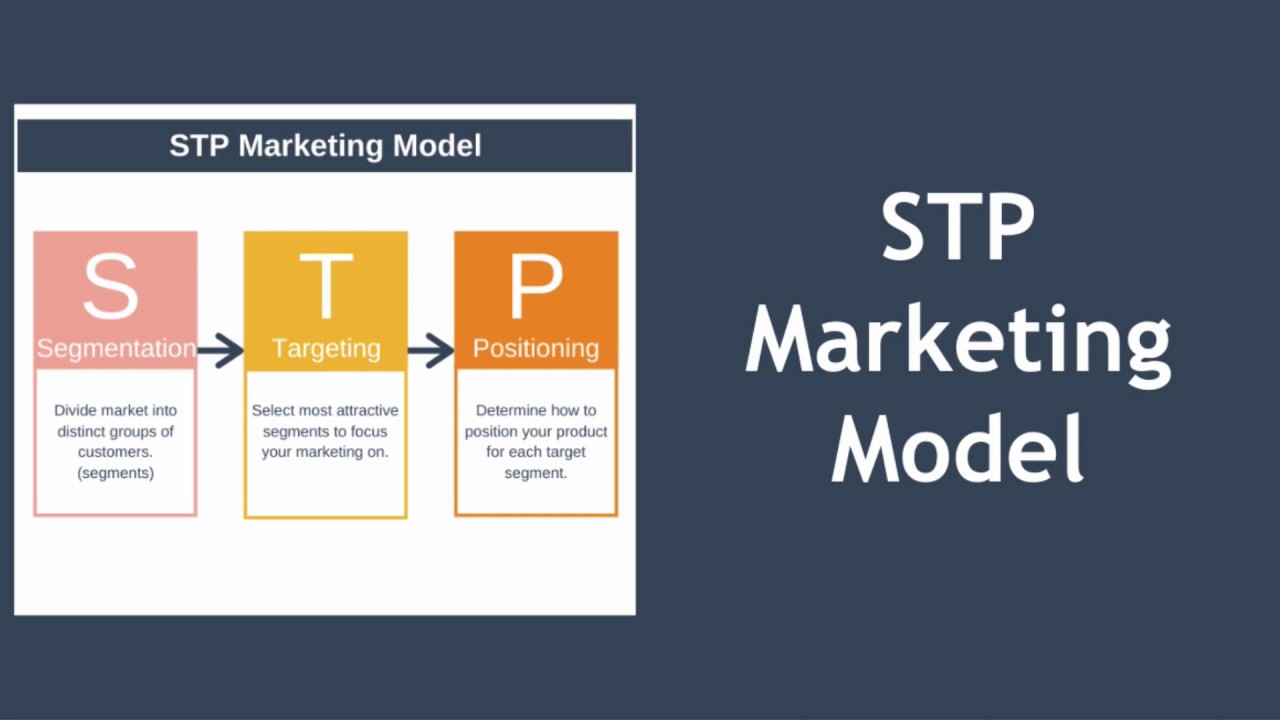
The STP marketing mix refers to a three-step model that involves segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
Segmentation involves dividing the market into smaller customer segments based on criteria such as geography, demographics, behavior, and psychographics.
Targeting focuses on specific customer segments with tailored marketing campaigns.
Positioning involves adjusting the marketing mix to meet the desires and expectations of the target audience.
STP marketing allows for hyper-personalization of brand messaging and enables businesses to compete with larger whole-market businesses.
It helps identify the most valuable customer segments and create products and marketing communications that specifically target those customers.
Overall, STP marketing offers benefits such as improved engagement, reduced marketing costs, and more focused product innovation.Key Points:
- STP marketing mix involves segmentation, targeting, and positioning
- Segmentation divides the market based on geography, demographics, behavior, and psychographics
- Targeting focuses on specific customer segments with tailored marketing campaigns
- Positioning adjusts the marketing mix to meet the desires and expectations of the target audience
- STP marketing allows for hyper-personalization and competition with larger whole-market businesses
- It helps identify valuable customer segments and create targeted products and marketing communications
- Benefits of STP marketing include improved engagement, reduced marketing costs, and focused product innovation.
Check this out:
💡 Did You Know?
1. The STP marketing mix, also known as the Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning marketing mix, was first introduced in the early 1950s by Wendell R. Smith, a professor of marketing at the University of Pittsburgh.
2. The STP marketing mix is a strategic approach that helps businesses identify specific market segments, select target markets, and position their products or services in a way that differentiates them from the competition.
3. The STP technique gained significant popularity in the 1980s due to the emergence of niche markets. It allowed businesses to focus their marketing efforts on smaller, more defined customer segments rather than broad and generic approaches.
4. Segmentation, the first step in the STP marketing mix, involves dividing the market into distinct groups based on certain characteristics or criteria such as demographics, psychographics, behavior, or geographic location.
5. Targeting, the second step in the STP marketing mix, involves selecting the most attractive and lucrative segment(s) to focus on. It requires businesses to evaluate the potential profitability, competition, and accessibility of each segment before making a strategic decision.
What Is STP Marketing And How Does It Work?
STP marketing stands for segmentation, targeting, and positioning. It is a three-step model that businesses use to develop effective marketing strategies. By understanding their target audience and tailoring their marketing efforts to meet the needs and desires of specific customer segments, companies can achieve greater success in their marketing campaigns.
Updated for 2025’s advertising best practices.
The STP model begins with segmentation, which involves dividing the market into distinct customer segments based on various criteria, such as demographics, geography, behavior, and psychographics. By segmenting the audience, businesses gain insight into the characteristics and preferences of different customer groups.
Once the segments are defined, the next step is targeting. Targeting involves selecting specific segments that align with the company’s objectives and focusing marketing efforts on these segments. By tailoring marketing campaigns to appeal to the chosen segments, businesses can increase their chances of success. This targeted approach allows companies to effectively reach and engage with their desired customers.
The final step in the STP model is positioning. Positioning involves adjusting the marketing mix to match the desires and expectations of the target audience. This includes aligning the product with the target audience, differentiating from competitors, highlighting benefits, emphasizing value for money, focusing on unique selling propositions, and showcasing prestige. By positioning their products or services effectively, businesses can create a favorable perception in the minds of their target customers.
Key points:
- STP marketing stands for segmentation, targeting, and positioning
- Segmentation involves dividing the market into distinct customer segments based on various criteria
- Targeting involves selecting specific segments that align with the company’s objectives
- Positioning involves adjusting the marketing mix to match the desires and expectations of the target audience
Importance Of Personalization In Marketing Decisions
Personalization plays a crucial role in marketing decisions as it directly influences customers’ shopping decisions. In today’s competitive market, customers expect personalized experiences and tailored messaging. When businesses understand their customers’ needs, habits, and preferences, they can create personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with individual customers, increasing engagement and ultimately driving sales.
- Personalization allows companies to deliver highly relevant and targeted content to their customers.
- By analyzing customer data and behavior, businesses can understand their customers’ preferences and provide them with personalized product recommendations, promotions, and messaging.
- This tailored approach makes customers feel valued and understood, leading to increased trust and loyalty.
Furthermore, personalization enables businesses to create a more seamless customer journey. By delivering personalized content across various touchpoints, businesses can ensure consistency and relevancy throughout the customer’s interactions. This creates a more cohesive and enjoyable customer experience, enhancing customer satisfaction and increasing the likelihood of repeat purchases.
“Personalization is essential in marketing decisions as it allows businesses to create meaningful connections with their customers, increase engagement, and drive sales.”
By understanding each customer’s unique needs and preferences, businesses can deliver personalized experiences that set them apart from their competitors and build long-lasting customer relationships.
- Bullet point 1
- Bullet point 2
- Bullet point 3
Segmentation: Identifying Customer Segments Based On Criteria
Segmentation is a critical step in the STP marketing model. It involves dividing the market into distinct customer segments based on various criteria. This allows businesses to gain a deeper understanding of their target audience and tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
There are several criteria that businesses can use for segmentation. Geography segmentation involves dividing the market based on geographic locations, such as countries, regions, or cities. Demographic segmentation focuses on characteristics such as age, gender, income, and education level. Behavioral segmentation divides customers based on their purchasing behavior, such as buying frequency, brand loyalty, or product usage. Psychographic segmentation considers customers’ personality traits, values, attitudes, and lifestyles.
By segmenting the audience, businesses can identify the most valuable customer segments and develop targeted marketing strategies for each segment. This allows them to address the unique needs and desires of each group, increasing the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Segmentation enables businesses to create personalized messaging and experiences for each segment. By understanding the characteristics and preferences of different customer groups, businesses can tailor their marketing materials, advertisements, and promotions to resonate with each segment. This personalization enhances customer engagement and increases the likelihood of conversion.
Overall, segmentation is a crucial step in developing an effective marketing strategy. By dividing the market into distinct customer segments, businesses can better understand their target audience, create personalized marketing campaigns, and ultimately drive sales.
Targeting: Tailoring Marketing Campaigns To Specific Customer Segments
Once the market has been segmented, the next step in the STP marketing model is targeting. Targeting involves selecting specific customer segments to focus marketing efforts on. By identifying the segments that align with the company’s objectives, businesses can direct their resources towards the most valuable and receptive audiences.
Targeting allows businesses to concentrate their marketing efforts on the segments that are most likely to convert into customers. By tailoring marketing campaigns to the specific needs and preferences of these segments, companies can increase the effectiveness of their messaging and improve their chances of driving sales.
To target specific customer segments effectively, businesses need to have a deep understanding of each segment’s characteristics and behaviors. By analyzing data and conducting market research, companies can gain insights into their target audience’s preferences, habits, and purchasing behavior. This information can then be used to develop targeted marketing strategies that address the unique needs of each segment.
Targeting also allows businesses to allocate their resources more efficiently. Instead of spreading their marketing efforts thinly across the whole market, companies can focus on the segments that offer the best potential for success. This targeted approach helps businesses make the most of their marketing budget and resources, maximizing their return on investment.
Overall, targeting is a crucial step in the STP marketing model. By selecting specific customer segments to focus on, businesses can tailor their marketing campaigns to meet the unique needs and preferences of each segment. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of success and enables companies to make the most of their resources.
Positioning: Adjusting The Marketing Mix To Match The Target Audience
Positioning is the final step in the STP marketing model. It involves adjusting the marketing mix to match the desires and expectations of the target audience. Positioning allows businesses to create a favorable perception in the minds of their customers and differentiate themselves from competitors.
There are several strategies that businesses can employ to position their products or services effectively. One strategy is aligning the product with the target audience by understanding their needs and preferences. By developing products or services that meet these specific requirements, businesses can position themselves as the solution to their customers’ problems.
Differentiating from competitors is another positioning strategy. By highlighting unique features or benefits that set the product apart from competitors, businesses can position themselves as the superior choice. This differentiation can be based on various factors such as quality, price, convenience, or innovation.
Emphasizing value for money is another effective positioning strategy. By showcasing the value and benefits that customers will receive in relation to the price they pay, businesses can position themselves as a cost-effective and valuable option.
Focusing on unique selling propositions (USPs) is also important in positioning. By identifying and promoting the unique aspects or advantages of the product, businesses can position themselves as the best option for customers seeking those particular benefits.
Additionally, positioning can involve showcasing prestige or exclusivity. By creating a perception of luxury, high quality, or rarity, businesses can position their products as desirable status symbols.
To effectively position their products or services, businesses need to analyze their competitors, identify their value propositions, and communicate them to customers. By understanding the market landscape and their competitors’ positioning strategies, businesses can adjust their own positioning to stand out in the minds of customers.
In summary, positioning is a crucial step in the STP marketing model. By adjusting the marketing mix to meet the desires and expectations of the target audience, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors, create a favorable perception, and increase their chances of success.
Benefits Of Using STP Marketing For Hyper-Personalization
STP marketing offers numerous benefits for businesses, particularly in terms of hyper-personalization. Hyper-personalization refers to highly targeted and tailored marketing strategies that create personalized experiences for individual customers. By leveraging the STP model, businesses can achieve a higher level of hyper-personalization, resulting in improved engagement, reduced marketing costs, and more focused product innovation.
One of the main advantages of using STP marketing for hyper-personalization is improved engagement. When businesses have a deep understanding of their target audience, they can create highly relevant and personalized content that resonates with individual customers. By delivering the right message to the right audience at the right time, companies can increase customer engagement and interaction with their brand.
STP marketing also allows businesses to reduce marketing costs. Instead of using broad and generic marketing campaigns that target a wide audience, businesses can focus their resources on specific customer segments that offer the best potential for conversion. This targeted approach helps companies make the most of their marketing budget and increase their return on investment.
Furthermore, STP marketing enables businesses to focus their product innovation efforts on the most valuable customer segments. By identifying their most profitable segments, businesses can develop products or services that specifically target the needs and preferences of these segments. This customer-centric approach ensures that resources are utilized efficiently and that innovation efforts are more likely to succeed.
In summary, STP marketing offers benefits such as improved engagement, reduced marketing costs, and more focused product innovation. By leveraging the STP model, businesses can achieve a higher level of hyper-personalization, resulting in increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profitability.
- Improved engagement
- Reduced marketing costs
- More focused product innovation.
STP Marketing For Small Businesses And Startups
STP marketing is particularly beneficial for small businesses and startups as it allows them to compete with larger whole-market businesses on a more even playing field. By leveraging the STP model, small businesses can identify their most valuable customer segments and create products and marketing communications that specifically target those customers. This targeted approach enables small businesses to compete effectively with larger competitors that may have more resources.
One of the key advantages of STP marketing for small businesses is the ability to tailor marketing campaigns and communications to the unique needs and preferences of their target audience. By understanding the characteristics and behaviors of their customers, small businesses can create personalized messaging and experiences that resonate with their target customers. This level of personalization helps small businesses build stronger relationships with their customers and gain a competitive edge.
STP marketing also allows small businesses to allocate their limited resources more efficiently. Instead of spreading their marketing efforts thinly across the entire market, small businesses can focus on specific customer segments that offer the best potential for success. By targeting these segments, small businesses can maximize their return on investment and compete effectively with larger, more established competitors.
Furthermore, the STP model enables small businesses to continuously refine their marketing strategies and stay agile in a rapidly changing market. By analyzing data and monitoring customer behavior, small businesses can make data-driven decisions and adjust their marketing efforts accordingly. This flexibility helps small businesses adapt to market trends and customer preferences, ensuring long-term success and growth.
In summary, STP marketing is highly advantageous for small businesses and startups. It allows them to compete effectively with larger competitors by tailoring marketing campaigns to specific customer segments, allocating resources efficiently, and staying agile in a rapidly changing market.
Steps To Creating A Marketing Strategy Using The STP Model
Creating a marketing strategy using the STP model involves several steps. These steps help businesses gain a deeper understanding of their target audience and develop strategies that effectively engage and convert their customers. The following outlines the steps to creating a marketing strategy using the STP model:
Market Definition: Begin by defining the market by breaking it down into smaller segments. This can be done using TAM (Total Addressable Market), SAM (Serviceable Available Market), and SOM (Serviceable Obtainable Market) definitions. TAM represents the total market demand for a product or service, SAM represents the portion of the TAM that a company can realistically address, and SOM represents the specific portion of SAM that a company can capture.
Audience Segmentation: Once the market has been defined, create audience segments based on various variables such as geography, demographics, behavior, and psychographics. Geographical segmentation involves dividing the market based on geographic locations. Demographic segmentation focuses on characteristics such as age, gender, income, and education. Behavioral segmentation considers purchasing behavior, brand loyalty, or product usage. Psychographic segmentation analyzes personality traits, values, attitudes, and lifestyles.
Target Audience Selection: After segmenting the audience, select the best-fit segments to target. This involves analyzing the segments based on factors such as size, growth potential, profitability, and alignment with the company’s objectives. Choose segments that offer the best potential for success and align with the company’s unique value proposition.
Positioning Analysis: Once the target audience has been identified, analyze the positioning strategies of competitors within the market category. Identify their value propositions, strengths, and weaknesses. This analysis will help the company develop a positioning strategy that differentiates itself from competitors and appeals to the target audience.
Positioning Strategy Development: Based on the analysis of competitors and the target audience’s desires and expectations, develop a positioning strategy that effectively communicates the unique value proposition of the company’s products or services. This may involve aligning the product with the target audience, highlighting benefits or value for money, focusing on unique selling propositions, or emphasizing prestige or exclusivity.
Marketing Mix Adjustment: Finally, adjust the marketing mix to align with the chosen positioning strategy. The marketing mix consists of the 4 Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. Ensure that the product or service meets the desires and expectations of the target audience. Determine the pricing strategy that is most appealing to the target audience and aligns with the company’s positioning. Select distribution channels and locations that allow the product to reach the target audience effectively. Develop promotional strategies and tactics that communicate the unique value proposition of the product and resonate with the target audience.
By following these steps, businesses can create a comprehensive marketing strategy using the STP model. This approach ensures that marketing efforts are focused, relevant, and effective in engaging and converting the target audience.
Positioning Strategies For Effective Marketing
Positioning is a crucial aspect of effective marketing. It involves communicating the unique value proposition of a product or service to the target audience and differentiating the company from competitors. To develop effective positioning strategies, businesses can consider various factors such as market category, customer desires, and the unique capabilities or advantages of the product or service.
The following are some common positioning strategies that businesses can use to enhance their marketing:
Aligning with the target audience: Position the product or service in a way that aligns with the desires and needs of the target audience. Understand the target audience’s pain points, challenges, and aspirations, and position the product as the solution to these needs. By aligning with the target audience, businesses can create a strong connection and increase the likelihood of conversion.
Differentiating from competitors: Highlight the unique features or benefits of the product or service that set it apart from competitors. Identify the unique selling propositions (USPs) and communicate them effectively to the target audience. This differentiation can be based on factors such as quality, price, convenience, innovation, or customer service.
Highlighting benefits: Emphasize the benefits that customers will gain by using the product or service. Clearly communicate the value and advantages that the product offers, and how it can improve the lives or solve the problems of customers. By focusing on benefits, businesses can create a compelling value proposition that resonates with the target audience.
Emphasizing value for money: Position the product or service as providing great value for money. Showcase the benefits and advantages that customers will receive in relation to the price they pay. Highlight the cost-effectiveness and quality of the product, and communicate why it is a wise investment.
Focusing on unique selling propositions (USPs): Identify the unique aspects or advantages of the product or service that distinguish it from competitors. Communicate these USPs clearly and effectively to the target audience. By focusing on these unique features or benefits, businesses can position themselves as the best option for customers seeking those particular advantages.
Showcasing prestige or exclusivity: Create a perception of luxury, high quality, or rarity.
These positioning strategies can help businesses effectively communicate the value of their products or services, differentiate themselves from competitors, and connect with their target audience.
FAQ
What is STP in the marketing mix?
STP in the marketing mix refers to Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning. Segmentation involves dividing the market into distinct groups based on their shared characteristics and needs. Targeting involves selecting specific segments to focus on based on their attractiveness and fit with the company’s objectives. Lastly, positioning involves developing a unique and compelling message to differentiate the company’s products or services in the minds of the target customers. By following the STP model, companies can effectively tailor their marketing efforts to reach the right customers with the right message, ultimately increasing their chances of success in the market.
What is the relationship between STP and 4Ps?
The relationship between STP and 4Ps is that STP, which stands for segmentation, targeting, and positioning, provides the foundation for developing the appropriate marketing mix within the 4Ps framework. STP helps identify the specific segments that offer the most value to a company, and based on this information, the 4Ps (product, price, place, and promotion) are tailored to meet the needs and preferences of those segments. In other words, STP guides the strategic decision-making process required to effectively utilize the 4Ps in targeting the right customers with the right offering.
What is an example of STP targeting?
One example of STP targeting can be observed in the automotive industry, specifically with car manufacturers like BMW. BMW uses the STP model to successfully target different customer segments. For instance, the company targets high-end customers who value luxury and performance by offering sleek and powerful cars like the BMW M5. On the other hand, BMW also targets environmentally conscious customers by offering electric and hybrid models like the BMW i3. By identifying and catering to the unique needs and preferences of different customer groups, BMW effectively adopts the STP approach to expand its market share and meet diverse customer demands.
Another example of STP targeting can be seen in the fashion industry, with brands like H&M. H&M utilizes the STP model to target various customer segments. For instance, H&M targets fashion-forward individuals who value affordability and current trends with their regular clothing line. Simultaneously, H&M also targets environmentally-conscious consumers with their sustainable clothing line, H&M Conscious. By adopting an STP approach, H&M is able to capture the interest and spending power of different customer groups, offering them products that align with their specific needs and values.
What are the 4 segmentation variables?
Segmentation variables are essential tools that marketers employ to divide their audience into distinct groups based on different characteristics. The four primary types of segmentation variables are demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral traits. Demographic segmentation focuses on factors such as age, gender, income, and occupation to understand consumer preferences and purchasing behavior. In geographic segmentation, marketers geographically classify their audience based on location, climate, or population density to target specific regions or customize marketing strategies accordingly. Psychographic segmentation delves into the psychological and sociological characteristics of consumers, including their values, lifestyles, and personalities. Lastly, behavioral traits segmentation takes into account consumer purchasing habits, loyalty, and usage patterns to understand and cater to their specific needs effectively.
Buy Traffic • Programmatic Advertising • Advertising Platform for Marketers