- rtb bidding strategies
- Cost Per Impression
- Flat Rate
- Tactic Reach
- Line Item Reach
- Campaign Reach
- Ctr (Click Through Rate)
- Clinical Behavior
- Audience Quality (AQ)
- Preferred Deals For Premium Ad Space
- Optimizing Bid Floors For Increased Revenue
- FAQ
- 1. How do real-time bidding (RTB) bidding strategies help advertisers optimize their ad spend?
- 2. What are some common RTB bidding strategies used by marketers to reach their desired target audience?
- 3. Can you explain the difference between first-price and second-price auctions in RTB bidding strategies?
- 4. How do dynamic bidding algorithms in RTB optimize bidding strategies based on real-time user data?
In the fast-paced world of online advertising, RTBbiddingstrategies hold the key to unlocking success.
New insights from FroggyAds platform analytics.
From the cost per impression to audience quality, these strategies are carefully crafted to target the right audience at the right time.
In this article, we delve into the exciting world of RTB bidding strategies and explore how they optimize ad campaigns.
Let’s dive into the world of real-time bidding and discover the secrets behind its success.
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | Unleashing Powerful RTB Bidding Strategies: Mastering Programmatic Advertising |
| Category | Ads |
| Key takeaway | In the fast-paced world of online advertising, RTB bidding strategies hold the key to unlocking success.New insights from FroggyAds platform analytics. |
| Last updated | December 30, 2025 |
rtb-bidding-strategies">rtbbidding strategies
RTB bidding strategies refer to the methods used to determine how much advertisers are willing to pay for ads in real-time bidding auctions.
Some common RTB bidding strategies include Cost per Impression, Flat Rate, Tactic Reach, Line Item Reach, Campaign Reach, CTR (Click Through Rate), Clinical Behavior, and Audience Quality (AQ).
These strategies help advertisers optimize their ad campaigns and reach their target audience effectively.
It is essential for companies using RTB to stay updated on industry trends and adapt their strategies accordingly to maximize ROI and revenue opportunities.Key Points:
- RTB bidding strategies determine how much advertisers are willing to pay for ads in real-time bidding auctions.
- Common RTB bidding strategies include Cost per Impression, Flat Rate, Tactic Reach, Line Item Reach, Campaign Reach, CTR (Click Through Rate), Clinical Behavior, and Audience Quality (AQ).
- These strategies help advertisers optimize their ad campaigns and effectively reach their target audience.
- Companies using RTB need to stay updated on industry trends and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- The goal is to maximize ROI and revenue opportunities.
- Adapting RTB bidding strategies is essential for companies to stay competitive.
Check this out:
💡 Did You Know?
1. The term “rtb,” which stands for Real-Time Bidding, refers to the buying and selling of online ad impressions in real-time auctions. It allows advertisers to bid on each impression individually, targeting specific audiences and optimizing their ad spend.
2. The first successful real-time bidding auction took place in 2009 by advertising exchange platform, OpenX, which resulted in a significant shift in the digital advertising industry.
3. One interesting rtb bidding strategy is called the “second-price auction.” In this method, the highest bidder wins the auction but only pays the amount of the second-highest bid, promoting competitive bidding and maximizing value for the buyer.
4. Another bidding tactic frequently used in rtb is “dynamic pricing.” This strategy involves adjusting the bid value in real-time based on factors such as time of day, user demographics, and ad placement, allowing advertisers to optimize their bids for maximum effectiveness.
5. Some advertisers use a bidding strategy called “retargeting,” which aims to show ads to users who have previously interacted with their website or brand. This technique leverages user data and helps improve conversion rates by targeting audiences that have already shown interest.
Cost Per Impression
One of the most common RTB bidding strategies is Cost Per Impression (CPI). With CPI, advertisers set a fixed bid for each thousand impressions their ad receives. This strategy is suitable when brand exposure is the primary goal, as it allows advertisers to efficiently manage their budget and control the number of impressions their ads receive.
However, it is crucial to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as click-through rates (CTR) and conversion rates to evaluate the effectiveness of CPI as a bidding strategy.
- CPI is a common RTB bidding strategy
- Advertisers set a fixed bid for each thousand impressions
- Suitable for brand exposure as it allows budget management and control over impressions
- Important to monitor CTR and conversion rates to evaluate effectiveness of CPI as a bidding strategy.
Flat Rate
Another popular RTB bidding strategy is the Flat Rate model. In this approach, advertisers negotiate a fixed price with publishers for a specified ad placement or duration. Flat Rate provides predictability in terms of costs and enables advertisers to secure high-value placements without the uncertainty of real-time bidding. Advertisers should carefully analyze their target audience, campaign objectives, and available budget before opting for this strategy.
Tactic Reach
Tactic Reach is a bidding strategy that emphasizes reachingspecific audiences or target segments. Advertisers can utilize audience segmentation based on various parameters such as demographics, interests, location, or behavior, to ensure that their ads are served to the most relevant users. This strategy requires a deep understanding of your target audience and the effective utilization of data insights. By customizing ads for specific user groups, advertisers can greatly enhance ad performance and improve overall campaign success.
- Tactic Reach focuses on reaching specific audiences or target segments
- Audience segmentation can be based on demographics, interests, location, or behavior
- Tailoring ads to specific user groups can greatly improve ad performance and campaign success.
Line Item Reach
Line Item Reach aims to maximize the reach of an advertising campaign by utilizing multiple line items or ad creatives simultaneously. By diversifying ad creatives and capitalizing on the strengths of each, advertisers can increase the chances of reaching their target audience effectively. This strategy allows for greater testing and optimization opportunities while maintaining control over the overall reach of the campaign.
Campaign Reach
Campaign Reach strategy involves setting specific reach goals for an entire campaign. Advertisers can optimize their bids to ensure maximum exposure and achieve the desired reach among their target audience. This approach requires careful planning, including defining target reach goals, understanding campaign objectives, and monitoring performance closely to make necessary adjustments during the campaign.
Ctr (Click Through Rate)
Click Through Rate (CTR) measures the effectiveness of an ad by calculating the percentage of users who click on it after seeing it. Optimizing for CTR is vital for maximizing the performance of RTB campaigns. Advertisers can achieve higher CTRs by crafting compelling ad copy, utilizing eye-catching visuals, and strategically placing their ads in relevant websites or apps. Regular monitoring and testing different variations of ads can help improve CTR and drive better campaign results.
Clinical Behavior
Clinical Behavior is a bidding strategy that utilizes user behavior data to optimize ad targeting and bidding decisions. By analyzing user interactions, such as browsing history, purchasing patterns, or social media activity, advertisers can predict and influence user behavior. This enables the creation of highly personalized and targeted ads, which are more likely to resonate with the user, resulting in increased engagement and conversion rates.
Audience Quality (AQ)
Audience Quality (AQ) is a critical consideration when implementing RTB (Real-Time Bidding) bidding strategies. Advertisers should strive to target high-quality audiences that are more likely to engage with their ads and convert into customers. Evaluating audience quality involves analyzing parameters such as:
- Demographics
- Interests
- Previous online behaviors
- Purchase history
By ensuring ads are served to the most relevant and valuable audience segments, advertisers can maximize the return on their ad spend.
“Ad targeting should be focused on delivering ads to high-quality audiences to optimize campaign performance.”
Preferred Deals For Premium Ad Space
Preferred deals offer a valuable opportunity for publishers and advertisers to negotiate a set price for premium ad space. This direct communication between the two parties allows for greater control over ad placement and ensures reliable access to high-quality inventory. By securing premium ad placements at competitive prices, advertisers can significantly enhance the visibility and performance of their campaigns. Building strong relationships with publishers and exploring preferred deal arrangements can be a significant advantage in the competitive RTB landscape.
Optimizing Bid Floors For Increased Revenue
Optimizing bid floors is crucial for maximizing programmatic ad revenue. Bid floors represent the minimum price that advertisers are willing to pay for each impression. Setting bid floors too high can result in missed opportunities, while setting them too low may attract low-quality inventory or limit ad reach. Advertisers should regularly monitor bid floors and make data-driven adjustments to strike the right balance between revenue optimization and campaign objectives. Additionally, leveraging soft price floors (SPF) can further prevent missed opportunities while requiring more frequent optimization to stay competitive.
RTB bidding strategies play a pivotal role in the success of programmatic advertising campaigns. Advertisers must stay up-to-date with industry trends, understand their target audience, and constantly optimize their bidding strategies to adapt to market dynamics. By mastering these strategies and implementing them effectively, advertisers can unleash the full potential of real-time bidding, maximize their ROI, and achieve their advertising goals in the ever-evolving digital advertising landscape.
FAQ
1. How do real-time bidding (RTB) bidding strategies help advertisers optimize their ad spend?
Real-time bidding (RTB) bidding strategies help advertisers optimize their ad spend by allowing them to target specific audiences in real-time auctions. Advertisers can set their maximum bid and target parameters, such as demographics, interests, and location. As the auction progresses, the bidding algorithm evaluates each impression and places a bid based on the advertiser’s strategy and the value they assign to each impression. This allows advertisers to bid on impressions that are most likely to be valuable to their campaign, ensuring that their ad spend is directed towards the most relevant and high-performing opportunities. By continuously refining their bidding strategies based on real-time data and performance insights, advertisers can maximize their return on investment and optimize their ad spend.
2. What are some common RTB bidding strategies used by marketers to reach their desired target audience?
Some common RTB (real-time bidding) bidding strategies used by marketers to reach their desired target audience include first-price bidding and second-price bidding.
First-price bidding is a strategy in which marketers submit the highest bid they are willing to pay for an ad impression, and if they win, they pay the exact amount of their bid. This strategy is simple and straightforward but can result in overpaying for impressions.
On the other hand, second-price bidding involves marketers submitting a bid for an ad impression, and if they win the auction, they pay the price of the second-highest bid plus a small increment. This strategy encourages marketers to bid what they think the impression is worth and avoids overpaying for impressions. The second-price bidding strategy is widely used in RTB auctions.
3. Can you explain the difference between first-price and second-price auctions in RTB bidding strategies?
In real-time bidding (RTB) strategies, first-price and second-price auctions refer to different ways of determining the winning bid and the price to be paid by the winner.
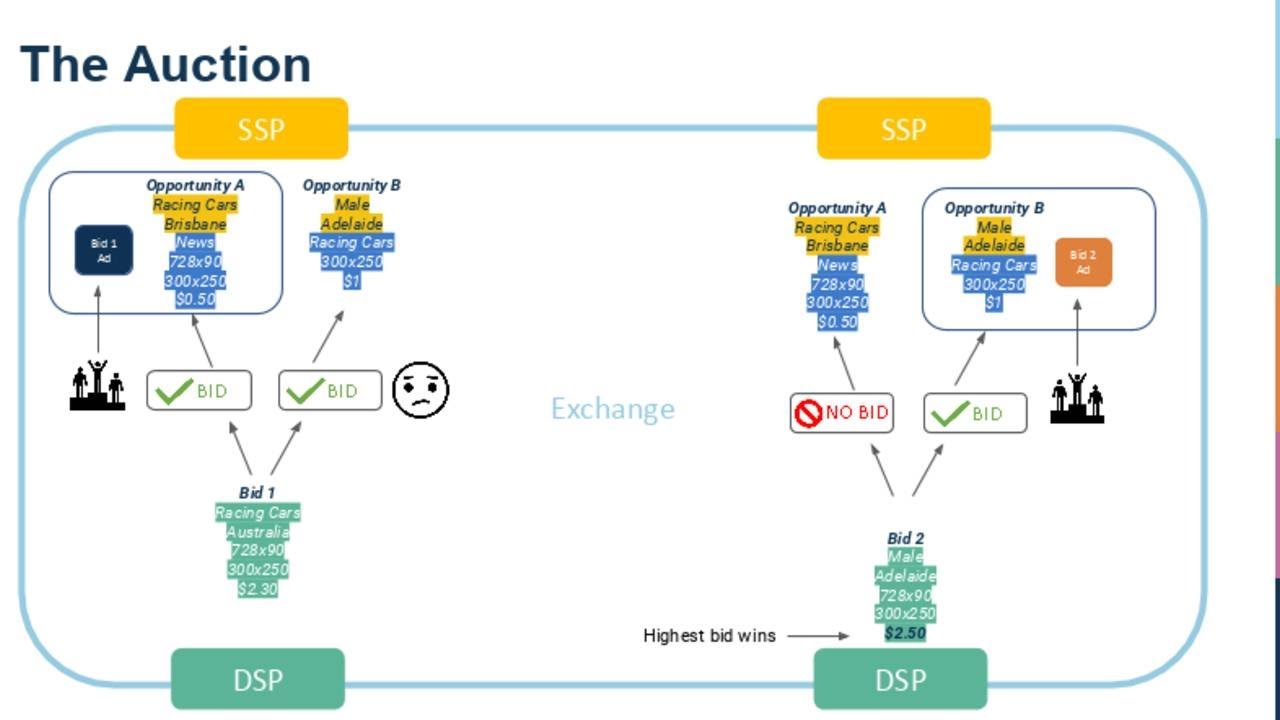
In a first-price auction, the highest bidder wins the auction and pays their own bid amount as the final price. For instance, if bidder A places a bid of $10, and bidder B places a bid of $8, then bidder A would win the auction and pay their bid of $10. This type of auction encourages bidders to submit their true valuation because they know they will only pay what they bid.
On the other hand, in a second-price auction, the highest bidder wins the auction, but they pay the price equal to the second-highest bid. For example, if bidder A bids $10, and bidder B bids $8, then bidder A would still win the auction but only pay $8, which is the bid of the second-highest bidder. This type of auction encourages bidders to bid their true valuation and avoid overpaying, as the price they actually pay is determined by the competitor’s bid.
4. How do dynamic bidding algorithms in RTB optimize bidding strategies based on real-time user data?
Dynamic bidding algorithms in real-time bidding (RTB) use real-time user data to optimize bidding strategies. These algorithms constantly analyze and evaluate user data, such as browsing behavior, demographics, and purchase history, to determine the likelihood of a user converting and the value of a potential impression.
Based on this data, the algorithm adjusts the bidding strategy in real-time to make more informed bidding decisions. For example, if a user has a high likelihood of converting, the algorithm might increase the bid to maximize the chance of winning the impression. Conversely, if a user is less likely to convert, the algorithm may lower the bid to minimize wasted spend.
By continuously analyzing and adapting to real-time user data, dynamic bidding algorithms enable advertisers to optimize their bidding strategies and allocate their budgets more effectively, resulting in higher conversion rates and improved return on investment (ROI).
Self-Serve DSP Platform • Buy Traffic • Native Ad Network • Programmatic Advertising • Advertising Platform for Marketers