- real time bidding diagram
- 1. Real-Time Bidding (RTB)
- 2. OpenRTB (oRTB)
- 3. IAB Tech Lab
- 4. Programmatic Advertising
- 5. Supply Side and Demand Side
- 6. Publishers and Ad Inventory
- 7. Supply Side and Demand Side Platforms
- 8. Ad Exchanges and Bidding
- 9. OpenRTB Mobile and OpenRTB Protocol
- 10. Connected TV (CTV) and OpenRTB Versions
- FAQ
- What is real-time bidding mechanism?
- What is the difference between RTB and oRTB?
- What is real-time bidding business model?
- What is real-time bidding terms?
In the vast digital advertising landscape, real-time bidding (RTB) has emerged as a powerful tool enabling advertisers to deliver personalized ads to their target audiences in the blink of an eye.
However, the intricacies behind this innovative process might leave you perplexed.
Fear not!
Join us on an enlightening journey as we unravel the mysteries of real-time bidding with the aid of a captivating diagram.
Prepare to dive into the terminology of OpenRTB, programmatic advertising, and ad exchanges, and unravel the secrets that shape the modern world of advertising.
Updated for the new year’s advertising best practices.
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | Real Time Bidding Diagram: Enhancing Efficiency in Ad Exchanges |
| Category | RTB |
| Key takeaway | In the vast digital advertising landscape, real-time bidding (RTB) has emerged as a powerful tool enabling advertisers to deliver personalized ads to their target audiences in the |
| Last updated | December 30, 2025 |
diagram">real time bidding diagram
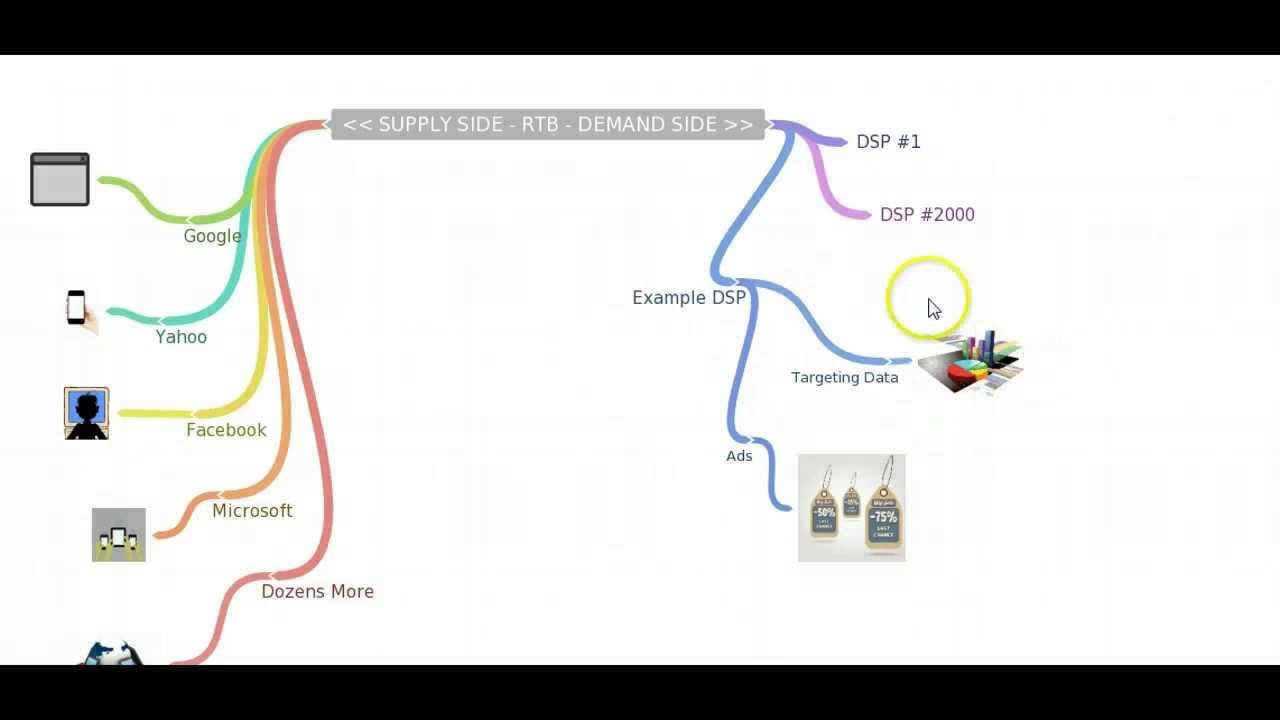
A real-time bidding diagram illustrates the process of programmatic advertising through the OpenRTB (oRTB) protocol.
In this diagram, the ad inventory of publishers or sites is made available through supply side platforms (SSPs) to potential advertisers.
On the demand side, advertisers access this inventory through demand side platforms (DSPs) to place bids on ad impressions in real-time.
These bids are then sent through ad exchanges to be matched with available impressions, based on parameters such as the target audience, ad placement, and bid price.
Bidders participate in the auction process, where the highest bids win and are displayed to users in real-time.
The OpenRTB protocol, which can be in versions such as 2.6, 2.5, 2.4, 2.3, 2.2, 2.1, 2.0, or even 1.0, facilitates the communication between SSPs, DSPs, ad exchanges, and bidders, ensuring interoperability.
This process allows for efficient and automated bidding, targeting, and delivery of ads, enhancing performance and effectiveness in mobile advertising, display campaigns, video ads, and connected TV (CTV).Key Points:
- Real-time bidding diagram explains programmatic advertising using the oRTB protocol
- Ad inventory is made available by publishers through SSPs
- Advertisers access the inventory through DSPs to place real-time bids on ad impressions
- Bids are sent through ad exchanges to match with available impressions based on parameters
- Bidders participate in an auction process where highest bids win and are displayed in real-time
- OpenRTB protocol facilitates communication between SSPs, DSPs, ad exchanges, and bidders
Check this out:
💡 Did You Know?
1. Real-time bidding (RTB) was officially introduced in 2009 as a new method for buying and selling online advertising inventory, revolutionizing the digital advertising industry.
2. The concept of real-time bidding diagram bases its principles on complex algorithms and artificial intelligence, allowing advertisers to bid on ad impressions in real-time, optimizing campaign performance by targeting specific audiences.
3. Not many people know that the first real-time bidding diagram was based on a modified version of the Vickrey auction model, which is a type of sealed-bid auction where participants submit independent and private bids.
4. Real-time bidding diagrams can process thousands of ad impressions per second, granting advertisers almost instantaneous access to publishers’ inventory on various websites, mobile apps, and other digital platforms.
5. Although real-time bidding has gained significant popularity in digital advertising, it still remains a somewhat mysterious and intricate process for many marketers and advertisers, as the algorithms and decision-making processes behind it are incredibly complex and constantly evolving.
1. Real-Time Bidding (RTB)
Real-Time Bidding (RTB) is a programmatic advertising approach that enables advertisers to bid for ad placements in real-time. It takes place in ad exchanges, where publishers sell their ad inventory and advertisers bid on these impressions. The goal of RTB is to automate the buying and selling of online advertising, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
In a typical RTB scenario, when a user visits a website or mobile app, an ad impression is generated. This impression is then sent to an ad exchange, where it becomes available for potential buyers. Advertisers utilize Demand Side Platforms (DSPs) to place bids on these impressions. They can specify their desired targeting criteria and set a maximum bid price.
Improvements:
- Added emphasis on RTB for clarity.
- Defined DSPs to provide more information.
2. OpenRTB (oRTB)
- OpenRTB (Open Real-Time Bidding) is a protocol developed by the IAB Tech Lab to standardize communication between buyers (advertisers) and sellers (publishers) in the RTB ecosystem.
- It provides a common language and set of rules for exchanging information such as bid requests, bid responses, and other parameters.
- OpenRTB ensures interoperability and transparency, enabling seamless integration between platforms and optimizing the efficiency of the ad buying process.
OpenRTB supports multiple versions, with the latest being version 2.6. Each version introduces new features, improvements, and bug fixes to enhance the functionality and security of the protocol. OpenRTB can be implemented using different data interchange formats, such as Protocol Buffers (ProtoBuf) or JSON.
Key points:
- OpenRTB is a protocol for communication between advertisers and publishers in the RTB ecosystem.
- It standardizes the exchange of bid requests, bid responses, and other parameters.
- OpenRTB ensures interoperability and transparency, optimizing the ad buying process.
- The latest version is 2.6, which introduces new features, improvements, and bug fixes.
- It can be implemented using Protocol Buffers (ProtoBuf) or JSON.
3. IAB Tech Lab
The IAB Tech Lab, short for Interactive Advertising Bureau Technology Laboratory, is a non-profit research and development consortium that drives the adoption of industry standards and best practices in digital advertising. The Tech Lab is responsible for the development and maintenance of the OpenRTB protocol, ensuring its compatibility with evolving technologies and meeting the needs of the advertising ecosystem stakeholders.
The IAB Tech Lab collaborates with industry experts, including publishers, advertisers, and technology vendors, to address challenges and drive innovation in the programmatic advertising space. Their efforts focus on areas such as ad fraud prevention, ad quality, data privacy, and cross-platform measurement.
4. Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is a method of buying and selling advertising space using automated technology and algorithms. This eliminates the need for manual negotiations and streamlines the process of ad placement. The use of real-time data and machine learning enables programmatic advertising to make data-driven decisions, optimizing both targeting and campaign performance.
By utilizing programmatic advertising, advertisers are able to effectively reach their target audience, while publishers can maximize their revenue by selling their ad inventory to the highest bidder. This method offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and scalability, allowing advertisers to deliver personalized and relevant ads to individual users across various channels and devices.
5. Supply Side and Demand Side
In the RTB ecosystem, there are two main players: the supply side and the demand side.
The supply side represents publishers who own ad inventory, such as websites or mobile apps, and want to monetize their content.
The demand side comprises advertisers who want to buy ad space to promote their products or services.
- Supply Side Platforms (SSPs) facilitate the selling of ad inventory on behalf of publishers. They connect publishers to ad exchanges and provide tools to manage and optimize their inventory.
- Demand Side Platforms (DSPs) enable advertisers to access ad exchanges, place bids on available impressions, and manage their campaigns.
SSPs and DSPs work together to facilitate the real-time buying and selling of ad impressions, ensuring efficient allocation and monetization of ad inventory.
- Real-time buying and selling of ad impressions
- Efficient allocation and monetization of ad inventory
6. Publishers and Ad Inventory
Publishers play a crucial role in the RTB (Real-Time Bidding) ecosystem as they provide the ad inventory where ads are displayed. Ad inventory refers to the available advertising space on websites, mobile apps, or other digital platforms. Publishers generate revenue by selling this ad inventory to advertisers through real-time bidding.
To maximize their revenue, publishers need to effectively manage their ad inventory. This includes setting pricing rules, targeting criteria, and ad format preferences. Publishers can also utilize tools such as Block Lists to prevent specific ads or advertisers from being displayed on their inventory. Additionally, they can leverage the Publisher Preferences API to communicate their inventory preferences to the SSPs (Supply Side Platforms) and ensure alignment with their advertising strategy.
7. Supply Side and Demand Side Platforms
Supply Side Platforms (SSPs) and Demand Side Platforms (DSPs) are key components of the Real-Time Bidding (RTB) ecosystem.
- SSPs enable publishers to connect their ad inventory with multiple demand sources, such as ad exchanges, advertisers, and DSPs.
They provide publishers with tools to manage and optimize their inventory, set pricing rules, and control the types of ads displayed.
DSPs enable advertisers to access multiple ad exchanges, gain insights into available ad inventory, and place bids on impressions that meet their targeting criteria.
- DSPs offer advanced targeting options, analytics, and campaign management tools to optimize ad performance and drive ROI.
SSPs and DSPs work together to facilitate the bidding process in real-time, matching the right ad impressions with the most relevant advertisers and ensuring efficient and effective ad delivery.
8. Ad Exchanges and Bidding
Ad exchanges play a crucial role in the RTB ecosystem. They serve as intermediaries, connecting publishers and advertisers in real-time. Through ad exchanges, publishers have the opportunity to offer their ad inventory, while advertisers can place bids to purchase impressions.
Bids are offers made by advertisers, indicating the maximum price they are willing to pay for a specific ad impression. These bids are evaluated and compared in real-time, empowering advertisers to make informed decisions based on factors like user data, targeting parameters, and campaign objectives. Ultimately, the highest bidder prevails, securing the opportunity to display their ad to the user.
Moreover, ad exchanges champion transparency and fair competition, creating a level playing field for all advertisers involved. They also offer support for various ad formats and targeting options, ensuring that advertisers can effectively reach their desired audience.
To summarize:
- Ad exchanges connect publishers and advertisers in real-time.
- Publishers can offer their ad inventory, while advertisers place bids to purchase impressions.
- Bids indicate the maximum price advertisers are willing to pay for specific ad impressions.
- Real-time bidding allows advertisers to make well-informed decisions.
- The highest bidder wins the auction and has their ad displayed to the user.
- Ad exchanges promote transparency and fair competition.
- They support various ad formats and targeting options to reach the desired audience effectively.
9. OpenRTB Mobile and OpenRTB Protocol
OpenRTB Mobile is an extension of the OpenRTB protocol that focuses specifically on mobile advertising. Mobile advertising has its own set of unique characteristics and requires specific parameters, including device type, location, and connection type. These parameters are essential for effective targeting and delivery of ads to mobile users.
The OpenRTB protocol, whether used for desktop or mobile, ensures compatibility and interoperability across various platforms and systems. It offers a standardized approach for exchanging bid requests, bid responses, and other parameters related to ad placements. By extending the capabilities of the protocol, OpenRTB Mobile addresses the specific requirements of mobile advertising, thereby boosting the efficiency and effectiveness of mobile ad campaigns.
To summarize:
- OpenRTB Mobile is an extension of the OpenRTB protocol for mobile advertising.
- Mobile advertising has unique characteristics and requires specific parameters.
- The OpenRTB protocol ensures compatibility and interoperability.
- OpenRTB Mobile enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of mobile ad campaigns.
“Mobile advertising has become an integral part of the digital marketing landscape. OpenRTB Mobile plays a crucial role in enabling advertisers to effectively target and deliver ads to mobile users by providing the necessary parameters and extending the capabilities of the OpenRTB protocol.”
10. Connected TV (CTV) and OpenRTB Versions
Connected TV (CTV) refers to televisions that are connected to the internet, allowing users to stream content from various online platforms. CTV has become an increasingly popular medium for advertisers to reach their target audience with targeted and engaging video ads.
The OpenRTB protocol has undergone multiple versions to adapt to evolving technologies and industry needs. OpenRTB versions 2.0 to 2.6 introduced various enhancements and improvements, including support for CTV advertising. Ad exchanges, DSPs, and SSPs leverage OpenRTB versions to enable seamless integration and communication between platforms.
By supporting CTV through OpenRTB, advertisers can extend their reach to the growing audience of streaming content viewers, while publishers can monetize their CTV inventory more effectively.
In summary, Real-Time Bidding (RTB) and the OpenRTB protocol have revolutionized the digital advertising industry. By implementing RTB and using OpenRTB to standardize communication, advertisers and publishers can enhance efficiency in ad exchanges, reaching their target audience with the right ads and maximizing revenue generation. The continuous evolution of OpenRTB versions ensures the adaptability of the protocol to emerging technologies and industry trends, making it a crucial component in programmatic advertising.
- Connected TV (CTV) allows users to stream content from various online platforms.
- OpenRTB versions 2.0 to 2.6 introduced enhancements and improvements, including support for CTV advertising.
- Ad exchanges, DSPs, and SSPs use OpenRTB versions to enable seamless integration and communication.
- Supporting CTV through OpenRTB helps advertisers engage with a growing audience and publishers monetize their inventory effectively.
FAQ
What is real-time bidding mechanism?
Real-time bidding (RTB) is a dynamic mechanism in the digital advertising industry that facilitates the instantaneous buying and selling of ad inventory. Unlike traditional methods, RTB operates in real-time, allowing advertisers to evaluate and bid on available impressions within a matter of seconds. This rapid process takes place on platforms like Authorized Buyers, where advertisers can quickly assess, place bids, and secure ad space based on their target audience and desired outcomes. Through the use of RTB, advertisers can efficiently maximize their advertising budgets and ensure optimal placement of ads.
What is the difference between RTB and oRTB?
RTB and oRTB both involve real-time bidding in the programmatic ecosystem, but they differ in terms of their scope and functionality. RTB refers to the overall process of transacting media in real-time between buyers and sellers. It encompasses the entire system, including the various programmatic entities involved in the bidding process.
On the other hand, oRTB specifically pertains to the standard communication protocol used for real-time bidding. It defines the rules and guidelines that allow programmatic entities to communicate and participate in the bidding process efficiently. oRTB ensures interoperability and transparency among the different platforms, making the real-time bidding system more effective and streamlined.
What is real-time bidding business model?
Real-time bidding (RTB) is a dynamic business model in programmatic advertising that operates on the cost per mille (CPM) pricing model. It involves the automated buying and selling of digital ad impressions in real-time auctions. Advertisers participate in these auctions and bid for ad impressions on websites or mobile apps based on their target audience and campaign objectives. The CPM pricing structure allows advertisers to pay for every thousand ad impressions they win in these auctions. This method enables advertisers to target specific audiences and optimize their advertising budgets based on performance.
RTB has revolutionized the digital advertising industry by introducing automation and real-time decision-making into the ad buying process. With the CPM model, advertisers have greater control over their spending as they only pay for impressions that align with their target audience. Simultaneously, publishers can maximize their ad revenue by auctioning off their available ad space to the highest bidder. RTB, powered by CPM, has transformed digital advertising into a more efficient and precise system, providing benefits to both advertisers and publishers in reaching their respective goals.
What is real-time bidding terms?
Real-time bidding (RTB) is a dynamic approach to programmatic media buying, where ads are bought and sold in real time through instant auctions on a per-impression basis. Utilizing a supply-side platform (SSP) or an ad exchange, RTB enables advertisers to bid on ad impressions in milliseconds, allowing for precise targeting and efficient allocation of advertising budgets. This data-driven and automated process enables advertisers to reach their target audience at the right time, in the right place, and with optimized pricing, making it a valuable tool in the digital advertising landscape.
Advertising Platform for Marketers • Native Ad Network • Self-Serve DSP Platform