- advertising networks in bgp
- Introduction To Advertising Networks In Bgp
- Static Neighbor Assignments And Network Commands In Bgp
- Exact Match Requirement For Advertised Routes In Bgp
- Anchoring Advertisements With Null Routes In Bgp
- Aggregate-Address Command: Bgp Vs. Rib Match Requirements
- Non-Exact Match: Network Vs. Aggregate-Address Command In Bgp
- Troubleshooting Resources For Bgp Issues
- Conclusion
Are you curious about the intricate web of advertising networks in BGP? Brace yourself for a captivating exploration of this fascinating realm where routes are advertised and connections established.
In this article, we will shed light on advertising networks in BGP and how they differ from other IGP’s. Prepare to delve into theworld of static neighbor assignments, null routes, and the ingenious use of the aggregate-address command.
Additionally, we will unveil a valuable troubleshooting resource for BGP issues that will leave you equipped with knowledge and solutions. So, fasten your seatbelts and embark on this exhilarating journey through the advertisingnetworks of BGP!
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | The fascinating world of advertising networks in BGP: |
| Category | Ads |
| Key takeaway | Are you curious about the intricate web of advertising networks in BGP? Brace yourself for a captivating exploration of this fascinating realm where routes are advertised and conne |
| Last updated | December 27, 2025 |
advertising-networks-in-bgp">advertising networks in bgp
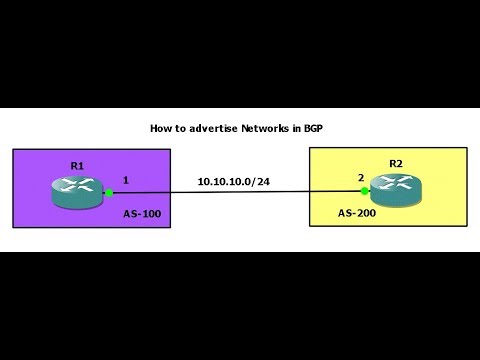
Advertising networks in BGP refers to the process of announcing routes to other Autonomous Systems (AS) in the Internet. Unlike other Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP), such as OSPF or EIGRP, BGP uses static neighbor assignments and the network command to advertise routes.
In BGP, for a network statement in the Routing Information Base (RIB) to be advertised, it requires an exact match. However, in some cases, a null route may be used to anchor the advertisement.
Optimized content based on recent advertiser behavior.
An interesting feature of BGP is the aggregate-address command, which requires a match in the BGP table rather than the RIB. Unlike the network statement, the network does not need to be an exact match with the aggregate-address command.
Troubleshooting BGP issues can be challenging, but there are resources available to help resolve them effectively.Key Points:
- Advertising networks in BGP involves announcing routes to other Autonomous Systems
- BGP uses static neighbor assignments and the network command to advertise routes
- A network statement in the RIB must have an exact match to be advertised, but a null route can be used in some cases
- The aggregate-address command in BGP requires a match in the BGP table, not necessarily an exact match
- Troubleshooting BGP issues can be challenging, but there are resources available for effective resolution.
Sources
https://networklessons.com/bgp/how-to-advertise-networks-in-bgp
https://networkengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/3249/injecting-routes-in-to-bgp-for-advertisement-bgp-network-command
https://afrozahmad.com/blog/how-to-advertise-routes-in-bgp/
https://www.flackbox.com/cisco-advertising-bgp-routes
Check this out:
💡 Pro Tips:
1. Use route filters to control the advertisements in BGP. Route filters can be implemented to allow or deny specific networks from being advertised, providing more control over the routing information exchange.
2. Implement prefix-lists and distribute-lists to fine-tune the advertisement process in BGP. These lists allow you to specify which prefixes to advertise or suppress based on various criteria such as IP address ranges, autonomous system numbers (ASNs), or tags.
3. Consider utilizing BGP communities for more targeted advertisements. BGP communities allow you to tag routes with specific attributes, such as geographical locations or customer groups, helping you control the propagation and behavior of advertisements within the BGP network.
4. Take advantage of route reflection or confederations to scale BGP advertisements in large networks. These techniques allow for a hierarchical structure in BGP deployments, reducing the number of full mesh peerings required and simplifying the advertisement process.
5. Regularly monitor and analyze BGP advertisements using tools like network monitoring systems or BGP-specific analysis platforms. These tools can provide insights into the routing behavior, help identify potential issues or misconfigurations, and optimize the advertisement process for better network performance.
Introduction To Advertising Networks In Bgp
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the fundamental routing protocol that enables the exchange of routing information between different autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. One essential aspect of BGP is the advertising of networks, which involves announcing the availability of certain network prefixes to neighboring routers.
Advertising networks in BGP operates differently compared to other Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP). Unlike IGPs such as OSPF or EIGRP, which use dynamic neighbor discovery mechanisms, BGP utilizes static neighbor assignments.
This means that BGP routers need to be manually configured with the IP addresses of their neighbors. Once the neighbors are configured, BGP uses the network command to advertise routes to these neighbors.
Static Neighbor Assignments And Network Commands In Bgp
In BGP, static neighbor assignments allow routers to establish specific relationships with their neighbors. This means that the IP addresses of the neighboring routers must be explicitly specified in the BGP configuration.
Once the neighbors are defined, the network command is used to advertise routes to these neighbors. The network command informs BGP which prefixes in the Routing Information Base (RIB) should be advertised to specific neighbors.
Exact Match Requirement For Advertised Routes In Bgp
Unlike some other routing protocols, BGP requires an exact match for the network statement in the RIB in order to advertise the associated routes. This means that BGP will only advertise routes that have an exact match with the network command in the RIB.
If a prefix in the RIB does not have an exact match with the network statement, it will not be advertised to BGP neighbors. This strict requirement ensures that only intended routes are propagated in the BGP routing domain.
Anchoring Advertisements With Null Routes In Bgp
In certain scenarios, a null route can be used to anchor BGP advertisements. A null route acts as a placeholder in the routing table for a specific prefix or network.
When a BGP router receives a packet for a network that has a null route, it will drop the packet instead of forwarding it. By anchoring an advertisement using a null route, it ensures that packets targeting that network are not accidentally forwarded.
Aggregate-Address Command: Bgp Vs. Rib Match Requirements
The aggregate-address command in BGP serves the purpose of summarizing multiple prefixes into a single prefix for advertisement.
However, it is important to note that the match requirements for this command differ between the BGP table and the RIB. In the BGP table, the aggregate-address command requires an exact match for the summarized prefix.
On the other hand, the RIB allows for more flexibility, allowing the summarized prefix to be less specific.
Non-Exact Match: Network Vs. Aggregate-Address Command In Bgp
A significant difference between the network and aggregate-address commands in BGP is their match requirements.
While the network command requires an exact match in the RIB, the aggregate-address command does not. This means that with the aggregate-address command, the advertised prefix can be less specific than the one in the RIB.
This flexibility allows network administrators to summarize their routing information and reduce the size of BGP tables without losing reachability to more specific prefixes.
Troubleshooting Resources For Bgp Issues
Troubleshooting BGP issues can be a complex task due to the protocol’s advanced features and interactions. However, there are several resources available to assist network administrators in resolving BGP-related problems.
One valuable resource is the BGP Troubleshooting Guide, which provides detailed steps and methodologies for diagnosing and resolving BGP issues. Additionally, online forums and communities dedicated to networking professionals can offer valuable insights and assistance in troubleshooting BGP problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, advertising networks in BGP differs from other Interior Gateway Protocols. BGP utilizes static neighbor assignments and the network command to advertise routes.
BGP requires an exact match for the network statement in the RIB for routes to be advertised. Null routes can be used for anchoring BGP advertisements.
The aggregate-address command in BGP has different match requirements compared to the RIB, allowing for summarization. Troubleshooting resources, such as the BGP Troubleshooting Guide, can be valuable in resolving BGP-related issues.
Understanding the intricacies of advertising networks in BGP is crucial for network administrators to effectively manage and troubleshoot BGP routing.
Programmatic Advertising • Advertising Platform for Marketers • Buy Traffic